It’s what, stress has become an inevitable part of daily life for many individuals. Whether it’s due to work pressures, financial concerns, relationship issues, or other stressors, the impact of stress can be significant and far-reaching. Understanding the physical symptoms of stress is crucial for recognizing when it’s time to take action and prioritize self-care.
Understanding Stress Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of stress is the first crucial step in managing its impact on our lives. Stress can manifest in various ways, affecting our physical health, emotional well-being, and behavior. By understanding these symptoms, we can better identify when stress is taking a toll and take proactive measures to address it. This section explores the physical, emotional, and behavioral symptoms of stress, providing a comprehensive overview to help you recognize and respond to stress effectively.
Physical Symptoms of Stress
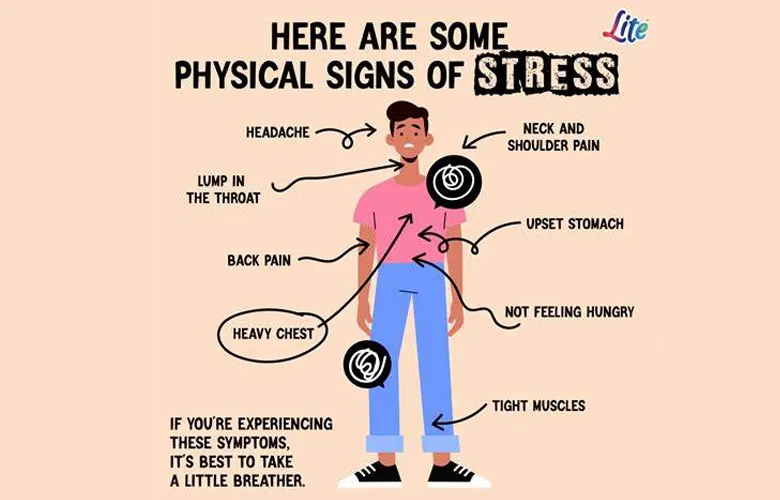
Stress often manifests itself in a variety of physical symptoms, serving as the body’s way of signaling that something isn’t quite right. These symptoms can range from mild discomfort to more severe health issues if left unaddressed. By paying attention to these physical cues, individuals can take proactive steps to manage stress and prevent it from escalating.
1. Headaches and Muscle Tension
One of the most common physical symptoms of stress is tension headaches. These headaches often manifest as a dull, aching pain around the forehead, temples, or back of the head. Muscle tension, particularly in the neck, shoulders, and jaw, is also prevalent among individuals experiencing stress. Prolonged muscle tension can lead to chronic pain and discomfort if not addressed promptly.
2. Fatigue and Sleep Disturbances
Stress can disrupt the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, leading to fatigue and sleep disturbances. Individuals may find it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep throughout the night, resulting in feelings of exhaustion and daytime drowsiness. Poor sleep quality can further exacerbate stress levels, creating a vicious cycle that impacts overall well-being.
3. Digestive Issues
The gut-brain connection means that stress can have a profound effect on digestive health. Common digestive issues associated with stress include stomachaches, bloating, constipation, or diarrhea. These symptoms may arise due to changes in appetite, alterations in gut motility, or increased sensitivity to gastrointestinal discomfort during periods of heightened stress.
4. Rapid Heartbeat and Chest Pain
In times of stress, the body’s “fight or flight” response is activated, leading to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. While this response is beneficial in short bursts, chronic stress can lead to persistent rapid heartbeat and chest pain. These symptoms can be alarming and may mimic signs of more serious cardiovascular conditions if left unaddressed.
5. Recognizing and Addressing Physical Symptoms
Recognizing the physical symptoms of stress is the first step toward effective stress management. By paying attention to the signals your body is sending, you can take proactive steps to address stress and prevent it from negatively impacting your health and well-being.
Simple self-care practices such as regular exercise, relaxation techniques (e.g., deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation), and maintaining a healthy diet can help alleviate physical symptoms of stress. Additionally, seeking support from a healthcare professional or mental health counselor can provide valuable guidance and resources for managing stress effectively.
Emotional Symptoms of Stress
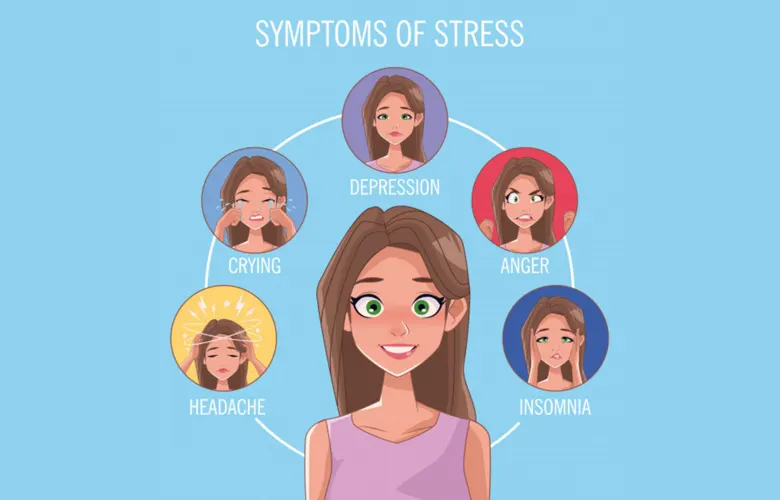

Stress is a complex phenomenon that affects not only our physical health but also our emotional well-being. In this section, we will explore the emotional symptoms of stress, shedding light on the various ways in which stress can impact our mental state. By understanding these emotional manifestations, individuals can better recognize when stress is taking a toll and take proactive steps to address it effectively.
1. Anxiety and Worry
Anxiety is a common emotional response to stress, characterized by feelings of apprehension, fear, and worry. Individuals may experience excessive worry about future events, ruminate over past mistakes, or feel on edge without a clear trigger. Physical symptoms such as racing heart, sweating, and trembling may accompany these feelings of anxiety, further exacerbating distress.
2. Irritability and Frustration
Stress can also manifest as irritability and frustration, leading individuals to become easily agitated, short-tempered, or prone to anger outbursts. Minor inconveniences or setbacks that would typically be manageable may trigger an exaggerated emotional response, straining relationships and exacerbating interpersonal conflicts. Chronic irritability can further contribute to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
3. Feelings of Sadness and Hopelessness
Prolonged exposure to stress can lead to feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and despair, which are hallmark symptoms of depression. Individuals may experience a persistent low mood, loss of interest in activities they once enjoyed, and difficulty experiencing pleasure. These feelings may be accompanied by changes in appetite, sleep disturbances, and thoughts of self-harm or suicide, necessitating immediate intervention and support.
4. Overwhelm and Helplessness
Stress often creates a sense of overwhelm, making individuals feel like they are drowning in responsibilities and unable to cope with life’s demands. This overwhelming sense of helplessness can lead to a loss of motivation, difficulty concentrating, and a feeling of being trapped in a cycle of stress and despair. Breaking free from this cycle requires acknowledging feelings of helplessness and seeking support to regain a sense of agency and control.
Behavioral Symptoms of Stress

Stress is not just a mental or emotional experience; it can also manifest in our behavior, influencing the way we act and interact with the world around us. In this section, we will explore the behavioral symptoms of stress, shedding light on the various ways in which stress can impact our actions and habits. By understanding these behavioral manifestations, individuals can better recognize when stress is taking a toll and take proactive steps to address it effectively.
1. Changes in Appetite
Stress can significantly affect appetite, leading to changes in eating habits that vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience an increase in appetite, turning to food as a source of comfort or distraction from stressors. This may result in overeating and weight gain. Conversely, others may lose their appetite altogether, experiencing nausea or digestive discomfort in response to stress, which can lead to weight loss and nutritional deficiencies.
2. Increased Substance Use
Another common behavioral response to stress is an increase in substance use, including alcohol, drugs, or tobacco. Individuals may turn to these substances as a way to cope with stress, seeking temporary relief from uncomfortable emotions or intrusive thoughts. However, reliance on substances as a coping mechanism can lead to dependency, addiction, and further exacerbation of stress-related problems.
3. Withdrawal from Social Activities
Stress can also lead to social withdrawal, causing individuals to isolate themselves from friends, family, and social gatherings. Feelings of overwhelm or a lack of energy may make social interactions feel exhausting or overwhelming, prompting individuals to retreat into solitude as a way to cope with stress. However, prolonged isolation can worsen feelings of loneliness and exacerbate stress-related symptoms.
4. Procrastination and Neglecting Responsibilities
Under stress, individuals may find it challenging to stay organized and motivated, leading to procrastination and neglect of responsibilities. Tasks that once seemed manageable may feel insurmountable, leading to avoidance and postponement of important deadlines or obligations. This procrastination can further increase feelings of stress and guilt, creating a vicious cycle that is difficult to break.
Impact of Untreated Stress
Untreated stress can have far-reaching consequences that extend beyond the immediate challenges it presents. In this section, we will explore the profound impact of allowing stress to go unaddressed, both on long-term health and on personal and professional aspects of life.

1. Long-term Health Consequences
Cardiovascular Diseases:
Chronic stress is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension, heart disease, and stroke. Prolonged activation of the body’s stress response system can lead to elevated blood pressure, inflammation, and damage to blood vessels, increasing the likelihood of developing cardiovascular problems over time.
Weakened Immune System:
Stress suppresses the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, illnesses, and autoimmune disorders. Chronic stress can impair the body’s ability to fight off pathogens and heal from injuries, leading to frequent illnesses and prolonged recovery times.
Digestive Disorders:
Stress can wreak havoc on the digestive system, contributing to a range of gastrointestinal problems such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), acid reflux, and ulcers. The gut-brain connection means that stress can exacerbate existing digestive issues and contribute to the development of new ones, leading to chronic discomfort and impaired nutrient absorption.
Mental Health Disorders:
Untreated stress is a significant risk factor for the development of mental health disorders such as anxiety disorders, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Chronic stress can alter brain chemistry, leading to imbalances in neurotransmitters associated with mood regulation and emotional well-being. Left unchecked, these mental health issues can significantly impact quality of life and functional impairment.
2. Effects on Personal and Professional Life

Strained Relationships:
Chronic stress can strain relationships with friends, family members, and romantic partners. Irritability, mood swings, and withdrawal from social activities can create tension and conflict, leading to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
Decreased Productivity and Performance:
Stress negatively impacts cognitive function, including memory, concentration, and decision-making abilities. In the workplace, untreated stress can lead to decreased productivity, poor performance, and difficulty meeting deadlines. This can jeopardize career advancement opportunities and lead to increased stress and job dissatisfaction.
Financial Difficulties:
Stress-related health problems, decreased productivity, and missed workdays can contribute to financial difficulties. Medical expenses, reduced income due to missed work, and additional expenses related to managing stress (such as therapy or medication) can strain finances and create additional stressors.
Impaired Decision-making Abilities:
Chronic stress can impair judgment and decision-making abilities, leading to impulsivity, indecisiveness, and poor choices. This can have consequences in both personal and professional contexts, affecting relationships, finances, and overall well-being.
Effective Stress Management and Treatment Options
In the face of stress, implementing proactive strategies to manage and alleviate its impact is crucial for maintaining overall well-being. In this section, we will explore various approaches to stress management and treatment options that have been proven effective in promoting resilience and reducing stress-related symptoms.
A. Lifestyle Changes
Healthy Diet
Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can provide essential nutrients that support overall health and resilience to stress. Avoiding excessive caffeine, sugar, and processed foods can help stabilize mood and energy levels.
Regular Exercise
Physical activity has been shown to reduce stress levels and improve mood by releasing endorphins, the body’s natural stress-relieving hormones. Engaging in regular exercise, whether it’s aerobic activities like jogging or cycling or mind-body practices like yoga or tai chi, can help combat the effects of stress on both the body and mind.
B. Psychological Interventions
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a highly effective therapeutic approach for managing stress and improving coping skills. Through CBT, individuals learn to identify and challenge negative thought patterns and develop adaptive strategies for managing stressors. CBT techniques can help individuals develop a more balanced perspective, build resilience, and regain a sense of control over their lives.
Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR)
MBSR is a mindfulness-based intervention that incorporates meditation, yoga, and mindfulness practices to reduce stress and enhance well-being. By cultivating present-moment awareness and acceptance of one’s thoughts and emotions, MBSR helps individuals develop greater resilience to stress and improve their ability to cope with life’s challenges.
C. Medical Treatments
Medication
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage stress-related symptoms such as anxiety or depression. Antidepressant medications, anxiolytics, and beta-blockers are among the medications commonly used to alleviate stress-related symptoms and promote emotional well-being. It’s important to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate medication and dosage for your individual needs.
Consultation with Healthcare Professional
Consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a primary care physician or mental health counselor, can provide valuable guidance and support in managing stress. A healthcare professional can help assess your stress levels, identify underlying factors contributing to stress, and develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your unique needs.
Final conclusion
Stress is an unavoidable aspect of modern life, but its impact can be significantly mitigated through awareness and proactive management. Understanding the multifaceted nature of stress.
its physical, emotional, and behavioral symptoms—is crucial in recognizing when it is taking a toll on our well-being. By identifying these symptoms early, individuals can take effective steps to manage stress before it leads to long-term health consequences or disrupts personal and professional life.
Implementing lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and ensuring sufficient sleep, can provide a strong foundation for stress resilience.
Psychological interventions like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) offer valuable tools for managing stress more effectively. In some cases, medical treatments and alternative therapies may be necessary to address more severe stress-related symptoms.